What is EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) | The Complete Guide
Welcome to our comprehensive Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) tutorial.
EDI is a revolutionary technology that has transformed the way businesses communicate.
It allows the transfer of data from one computer system to another by standardized message formatting, without the need for human intervention.
This guide will teach you the basics of EDI. You will learn what it is, why it is useful, and how to use it in different business situations.
Whether you are new to EDI or just want to learn more, this guide will show you how EDI can help make your business work better and faster.
What is EDI?
EDI is a structred method to send and receive documents and information electronically.
EDI helps companies to send and receive data such as purchase orders, invoices, inventory details, and shipping updates.
EDI removes the need of manual data entry which leads to less errors and faster work done.
This system is very important because it helps businesses share important details quickly and stay organized in today’s busy world.
What are the Types of EDI?
The types of EDI can be categorized based on how the electronic documents are transferred between companies. The three primary types of EDI are:
- Direct EDI (Point-to-Point): This involves the direct transmission of EDI documents between businesses through a secure communication protocol like FTPs, SFTP, or AS2. It requires both parties to maintain a constant connection. Typically large companies with lots of transactions use this.
- VAN (Value-Added Network): A VAN acts as an intermediary between companies that helps share EDI files. It also provides additional services, like keeping files safe and storing them until they’re delivered properly.
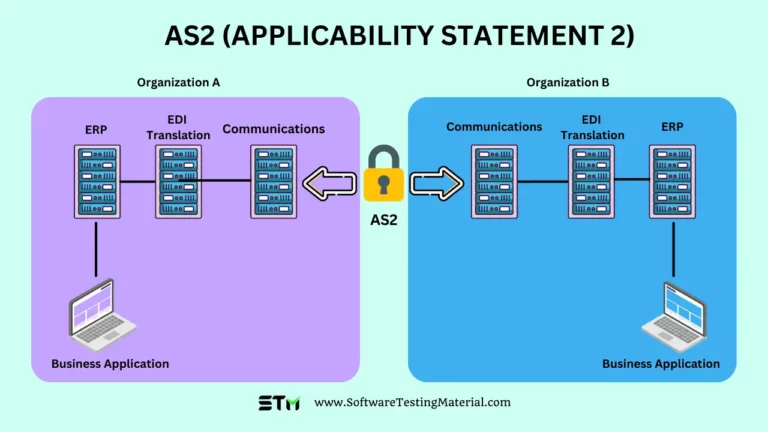
- EDI via AS2 (Applicability Statement 2): AS2 sends data safely over the Internet by wrapping it in a secure envelope. It’s popular because it uses HTTP and can send data directly while giving a receipt when delivery is successful.
- Web EDI: Web EDI lets smaller companies fill out forms or upload their EDI files online. It’s easy to use and doesn’t cost much, so it works well for businesses with fewer transactions.
- Mobile EDI: This is EDI for mobile devices. People can send and receive EDI files from their phones, making it easy to work while traveling.
By employing these various types of EDI, businesses can choose the most efficient and cost-effective method for their specific needs, ensuring seamless and secure communication in their trade partnerships.
What are the benefits of Electronic Data Interchange?
The benefits of EDI are as follows
#1. Saves Time & Money: EDI helps save time and money because it takes care of tasks automatically instead of using paper-based processes. It ensures instant delivery of business documents and helps people make faster decisions.
#2. Reduces Errors: EDI works automatically to avoid mistakes made by humans. It can find problems and fix them to make sure all documents are correct and follow the right format before being used.
#3. Improves Efficiency & Productivity: EDI makes work faster and easier by helping share and process lots of business documents quickly and correctly.
#4. Improves Traceability & Reporting: EDI helps track and record everything well. This makes it easier to keep customers happy by delivering products and services on time.
#5. Positive Customer Experience: By using EDI, businesses can track data better and get good information. This helps them to be more organized and give customers a better experience.
How Does EDI Work?
EDI operates by allowing the transfer of standardized data between different business systems or entities. It typically follows this multi-step process:

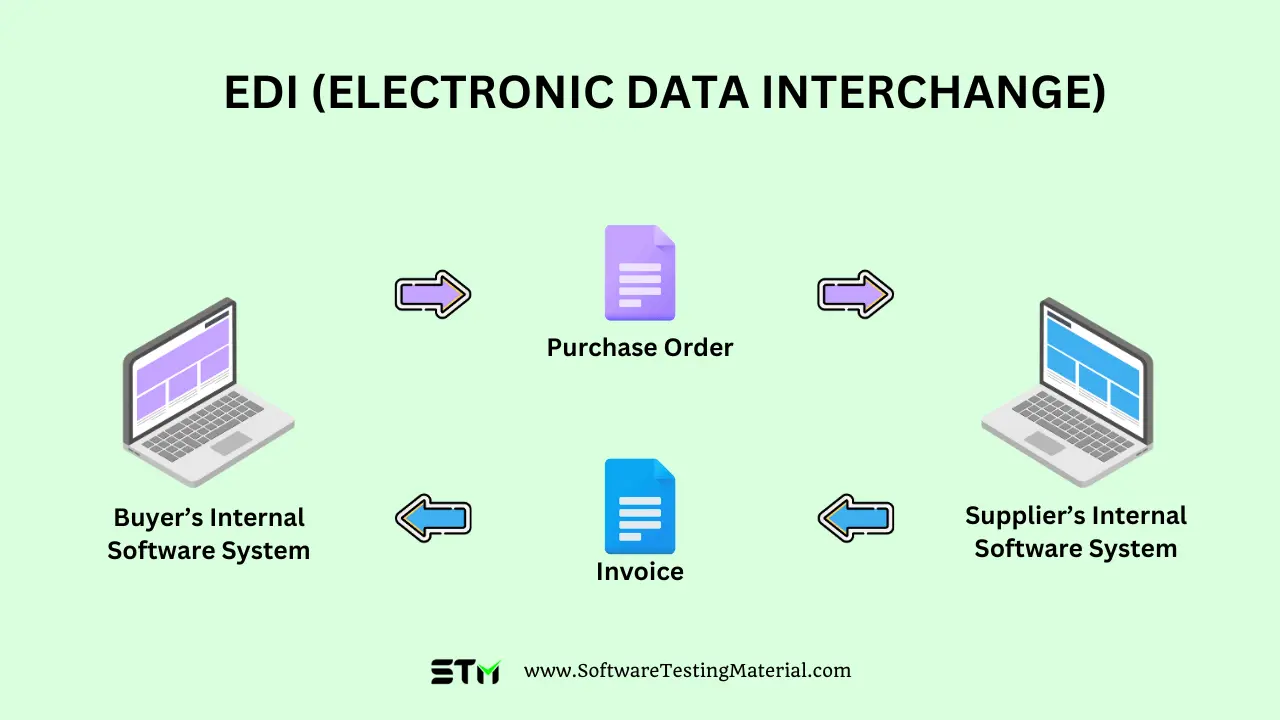
- Prepare the Documents: A buyer will collect and organize the data necessary for the transaction, such as a purchase order. This is often done through the buyer’s internal software systems.
- Convert to EDI Format: The organized data is then converted into an EDI format using one of the many EDI standards, such as ANSI ASC X12 or UN/EDIFACT. Some businesses use EDI software or employ an EDI service provider to translate the data.
- Transmit the EDI Document: Once converted, the EDI document is sent over a secure communication network, such as a VAN (Value-Added Network), or directly via protocols like AS2 or FTPs.
- Receive and Integrate: The supplier’s EDI system processes the incoming files. It translates them back into a format compatible with the supplier’s internal software systems. If it’s an order, for instance, it may directly populate their order management system.
- Action and Response: After integration, the supplier will carry out the appropriate action, such as dispatching goods or sending an invoice, and may send a return EDI document to confirm the action, like an order acknowledgment.
This streamlined communication process minimizes manual entry, speeds up business transactions, and reduces errors, all while allowing systems to interact regardless of their native languages or technologies.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the adoption of Electronic Data Interchange represents a substantial stride toward operational business excellence.
By automating the exchange of crucial business documents, companies can achieve unprecedented levels of accuracy, speed, and efficiency, leading to cost savings and improved business relationships.
As we’ve explored throughout this tutorial, EDI’s benefits are far-reaching, impacting various facets of an organization from supply chain management to customer satisfaction.
While the implementation of EDI may require careful planning and investment, the long-term advantages it provides are indisputable. We encourage businesses to embrace this transformative technology to maintain a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving digital marketplace.
Related posts:
- Best FTP Servers
- Best OFTP2 Server Tools
- Best File Transfer Automation Software in
- Best AS2 Software & Tools For Secure Electronic Data Interchange
- Best Secure File Transfer Software
- Best SFTP Automation Software
- What is an FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
- What is FTPS Server (File Transfer Protocol Secure)
- What is SFTP Server (Secure File Transfer Protocol)
- What is MFT (Managed File Transfer)
- What is SCP (Secure Copy Protocol)
- 14 Popular File Transfer Protocols For Business Explained
- What is AS2 (Applicability Statement 2)
- Best GoAnywhere Alternatives
- Best Globalscape Alternatives
- Best Digital Guardian DLP Alternatives
- Best Forcepoint DLP Alternatives
- Best Mcafee DLP Alternatives
- Best Symantec DLP Alternatives
- Best MOVEit Alternatives