What is FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
In the realm of data management and networking, File Transfer Protocol (FTP) serves as a critical cornerstone.
This article offers a comprehensive guide to understanding FTP, its functionalities, and its value in contemporary digital communication.
From its basic definition to its intricate workings, we will delve into every aspect of FTP, arming you with the knowledge you need to use this tool effectively.
Whether you are a seasoned IT professional or a novice in the field, this guide will offer insights into the importance and applications of File Transfer Protocol.
What is FTP
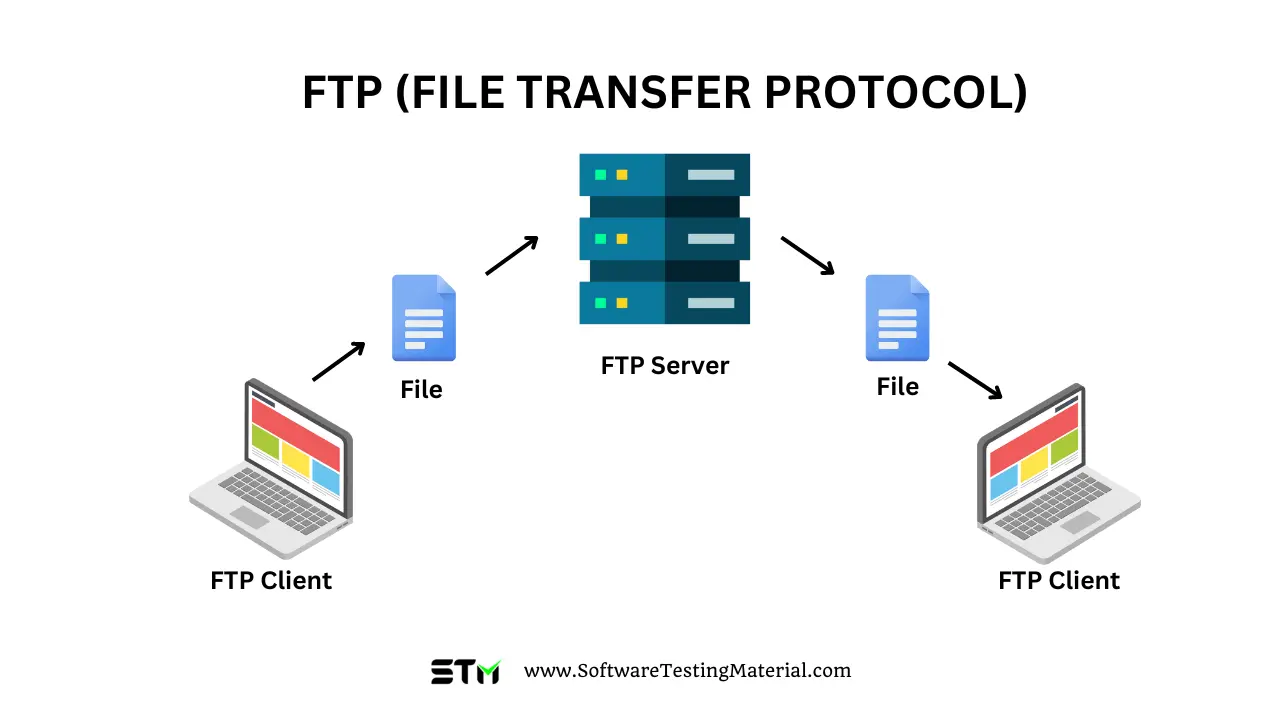
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard network protocol used for the transfer of computer files between a client and server on a computer network.
It was one of the earliest protocols developed for the internet and remains a powerful tool in the modern digital age.
FTP operates on a client-server model, where an FTP client application connects to an FTP server to perform operations such as uploading, downloading, or deleting files.
This protocol can facilitate large file transfers efficiently, making it a valuable tool for data management and digital communication.
What is the importance of FTP?
FTP’s importance lies in its ability to move large amounts of data securely and efficiently over the internet.
This feature is crucial in today’s digital age, where organizations and individuals often need to share large files or datasets.
By using FTP, they can ensure that these files are transmitted quickly and arrive intact at their destination.
Moreover, FTP can handle multiple file transfers simultaneously, making it a robust tool for managing and sharing data on a large scale.
In a nutshell, FTP plays a vital role in data management and digital communication by providing a reliable and efficient means of transferring large files over the internet.
What are the functionalities of FTP?
FTP possesses several key functionalities that contribute to its utility and efficiency.
Firstly, it allows for the transmission of both binary and text files between computers, eliminating the need for file type-specific transfer protocols.
Its structure supports the use of user IDs and passwords, ensuring the security of transfers and limiting access to authorized individuals.
FTP also permits the navigation of the server’s directory structure, allowing users to select specific files or folders for transfer.
Moreover, it supports the resumption of interrupted downloads, ensuring the integrity of large file transfers even in the face of connectivity issues.
Finally, FTP can perform multiple transfers concurrently, boosting efficiency when dealing with multiple files or large data sets.
Must read: Best FTP Servers
What are the Applications of the File Transfer Protocol?
FTP finds applications in a multitude of sectors due to its robust functionality and versatility.
In web development, it enables developers to upload files to their web servers directly from their local development environment.
In academia and research, FTP is instrumental in sharing large datasets, enabling collaborative work on complex projects.
Media organizations use FTP to distribute large multimedia files, including video and audio content, quickly and efficiently.
In the IT sector, FTP allows for the remote management and updating of software across networked systems.
Furthermore, FTP is used in backup and disaster recovery processes due to its ability to handle large file transfers.
These applications underscore the ubiquity and importance of FTP in today’s digital landscape.
How Does FTP Work?
FTP operates through a control connection and data connection, both established between the client and server. The control connection, initiated when the client logs in to the server, remains open throughout the FTP session to send control information (like commands and responses). The data connection, on the other hand, is opened and closed as required to transfer file data.
FTP uses two modes to transfer files – Active and Passive. In Active mode, the FTP server initiates a data connection to the client, whereas in Passive mode, it’s the client who initiates this connection.
FTP also employs two types of transmission modes – ASCII and Binary. ASCII mode is used for text, while Binary mode is used for non-text files (like images).
Hence, FTP’s workings involve a fine-tuned coordination between different connections, modes, and transmission types, ensuring efficient and secure file transfer between the client and server.
Is FTP Safe?
FTP, in its basic form, is not considered to be a secure method of data transfer because it lacks built-in encryption. This means that information can potentially be intercepted during transit and viewed by others.
However, there are variations of FTP like FTPS and SFTP, which incorporate encryption to provide a more secure data exchange. These protocols encrypt your data to protect it from prying eyes, making them a safer choice for transferring sensitive information.
Differences between FTP, FTPS, and FTPES
FTP or Vanilla FTP or plain FTP remains the standard way to transfer files over a network. It relies on two separate connections for control and data, and offers different types of modes for secure file transfer. By default, it uses port 21, and it is supported by the majority of web browsers.
FTPS (FTP Secure) is an extension of FTP which is more secure form of FTP, and is also known as FTP-SSL. As its name suggests, FTPS adds a layer of security to the FTP protocol by using SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocols to encrypt data. This means that any information exchanged through an FTPS connection is unreadable to unauthorized users.
FTPES (FTP with explicit SSL) is a form of FTP where SSL security is “explicitly” requested by the client and negotiated with the server.
The “E” in FTPES means “explicit,” making the acronym stand for File Transfer Protocol over explicit transport layer security (TLS)/SSL.
Some prefer FTPES over FTPS for several reasons. Primarily, its compatibility with firewalls makes it a more convenient choice for many users. Unlike FTPS, which can sometimes struggle with firewall settings, FTPES allows for smoother data transmission. Furthermore, FTPES offers flexibility, with the option for the client to choose whether to communicate securely or insecurely. This can be particularly beneficial in situations where full encryption isn’t necessary, thereby saving on computational resources. Lastly, as FTPES starts as a regular FTP using port 21, it then uses specific commands to upgrade to a TLS/SSL-encrypted transmission, making it a more adaptive protocol.
Each type serves different needs and is used based on factors like security requirements, type of data, and the purpose of file transfers.
FTPS vs. FTPES: Which Should You Use?
The choice between FTPS and FTPES hinges on your specific needs, the nature of the data being transferred, and the network environment.
FTPS, with its constant secure connection, is ideal when dealing with highly sensitive data where security is paramount.
On the other hand, FTPES offers a unique advantage with its flexibility, allowing you to switch between secure and insecure modes based on your requirements, which can save computational resources when full encryption isn’t necessary.
Additionally, FTPES’s superior compatibility with firewalls facilitates smoother data transmission, making it a convenient choice for many users.
Therefore, it’s essential to weigh these aspects before choosing the protocol that best suits your needs.
SFTP vs. FTPES: Which Should You Use?
The decision between SFTP and FTPES depends on your specific use case, the sensitivity of the data being transferred, and your network environment.
SFTP offers an all-in-one solution with its capabilities to handle file management and file transfers over an SSH connection, making it a comprehensive protocol for secure file transfers. However, FTPES is known for its flexibility, allowing the client to choose whether to communicate securely or insecurely, depending on the nature of the data and the necessity for encryption. This can be particularly beneficial for conserving computational resources when full encryption is not required. Furthermore, FTPES tends to be more compatible with firewalls, ensuring smoother data transmission.
Therefore, when choosing between SFTP and FTPES, it’s important to evaluate these factors and choose a protocol that best aligns with your data security needs and operational requirements.
What’s the Difference Between FTP and HTTP?
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) and HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) are two fundamental protocols used for transferring data over the internet, but they differ significantly. FTP, as its name suggests, is specifically designed for transferring files from one system to another. It establishes two connections between the host and the client – one for data transfer and the other for control information.
On the other hand, HTTP is the protocol used for transferring hypertext data over the World Wide Web. It’s the backbone of any data exchange on the Web and it’s a protocol used for transmitting hypermedia documents like HTML. Unlike FTP, HTTP uses a single connection for data transfer and it is stateless, meaning it doesn’t retain any record of previous user sessions.
FTP vs. MFT
| Features | FTP | MFT |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transfer Security | FTP does not have built-in encryption for data transfer, making it less secure. | MFT has built-in data encryption thus providing a higher level of security during data transfer. |
| File Size Limit | FTP has restrictions on the size of files that can be transferred. | MFT allows for the transfer of large files without size restrictions. |
| Reliability | FTP does not guarantee successful file transfer and does not provide detailed reports. | MFT has robust error handling and provides detailed reports on file transfer activities. |
| Automation | Automation is not inherent in FTP. | MFT supports automation of file transfers. |
| Compliance | FTP struggles to meet certain compliance requirements such as HIPAA or GDPR due to lack of security features. | MFT is designed to meet various compliance requirements as it includes features like data encryption and audit trails. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is an integral part of our digital world, offering powerful features for secure, efficient, and reliable file transfers.
Its versatility enables it to be applied across a range of sectors including web development, academia, media, and IT, enhancing collaboration and productivity.
As we continue to rely on the sharing and transfer of digital files for various operations, the relevance and importance of understanding how FTP works cannot be overstated.
By mastering FTP, individuals and institutions can significantly improve their data management and sharing capabilities, thus paving the way to a more connected and data-driven future.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does FTP Use TCP or UDP?
FTP utilizes the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) for its transport requirements, while User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is never employed.
How Does FTP Work?
FTP is a way to transfer files over the Internet. Just keep in mind that FTP transfers require an internet connection. To download a file, you’re moving it from a server to your computer or device. On the other hand, uploading means transferring a file from your computer to a server. So, it’s like sharing files back and forth!
What Is an Example of FTP?
There are several FTP clients to choose from, such as CoffeeCup Free FTP, Core FTP, FileZilla Client, FTP Voyager, and WinSCP.
What to Look for in an FTP Client
FTP clients offer various features for customizing file uploads and downloads. For example, if you’re using FileZilla, you can set bandwidth limits for your files. This way, you have control over the upload and download speeds, which can come in handy when managing multiple file transfers simultaneously.
When choosing an FTP client, you might also want to consider other features like public-key authentication, the option to adjust file compression levels, or tools that help you search a server using file masks.
Related posts:
- What is an FTPS Server (File Transfer Protocol Secure)
- What is an SFTP Server (Secure File Transfer Protocol)
- What is MFT (Managed File Transfer)
- What is SCP (Secure Copy Protocol)
- 14 Popular File Transfer Protocols For Business Explained
- What is AS2 (Applicability Statement 2)
- MFT Vs SSH: Whats the difference
- Difference between MFT vs SFTP