What is Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC) & STLC Phases
In this post, we’ll take you through everything you need to know about Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC). In the earlier post, we have learnt what is Software Testing and Software Development Life Cycle.
We’ll start with a Definition of STLC, STLC Phases and the following.
What is Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC)?
Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC) identifies what test activities to carry out and when to accomplish those test activities. Even though testing differs between organizations, there is a testing life cycle.
Don’t Miss: Manual Testing Complete Tutorial
STLC Video Tutorial
Check out the below video to watch “Software Testing Life Cycle Phases (STLC Phases)”
Phases of STLC
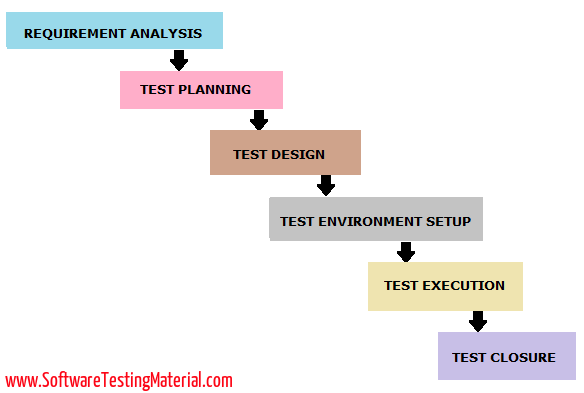
The different phases of the Software Testing Life Cycle Model (STLC Model) are:
- Requirement Analysis
- Test Planning
- Test Design
- Test Environment Setup
- Test Execution
- Test Closure
Every phase of STLC (Software Testing Life Cycle) has a definite Entry and Exit Criteria.
1. Requirement Analysis
The entry criteria for this phase is the BRS (Business Requirement Specification) document. During this phase, the test team studies and analyzes the requirements from a testing perspective.
This phase helps to identify whether the requirements are testable or not. If any requirement is not testable, the test team can communicate with various stakeholders (Client, Business Analyst, Technical Leads, System Architects, etc) during this phase so that the mitigation strategy can be planned.
What I do in Requirement Analysis Phase as a Software Tester?
As a software testers, When I start with the Requirement Analysis phase, my primary goal is to understand what needs to be tested. Here, I carefully go through the software requirements and specifications documents. If I have any doubts or need clarification, I talk to the stakeholders to make sure everything is clear. This phase helps me identify the testable requirements and the scope of testing.
Entry Criteria: BRS (Business Requirement Specification)
Deliverables: List of all testable requirements, Automation feasibility report (if applicable)
Must Read: Test Strategy In Depth Explanation
2. Test Planning
Test planning is the first step in the testing process.
In this phase typically Test Manager/Test Lead involves determining the effort and cost estimates for the entire project. Preparation of the Test Plan will be done based on the requirement analysis.
Activities like resource planning, determining roles and responsibilities, tool selection (if automation), training requirements, etc., carried out in this phase.
The deliverables of this phase are Test Plan & Effort estimation documents.
What I do in Testing Phase as a Software Tester?
In the Test Planning phase, I create a roadmap for how I will approach the testing process. This involves defining the objectives, resources, schedule, and scope of testing. I also decide on the tools and techniques we will use and prepare a high-level timeline. The test plan includes details about the testing environment, risk analysis, and contingency plans. It acts as a guide for executing the tests.
Entry Criteria: Requirements Documents
Deliverables: Test Strategy, Test Plan, and Test Effort estimation document.
Must Read: How To Write A Good Test Plan
3. Test Design
The test team starts with test case development activity here in this phase. Testers prepares test cases, test scripts (if automation), and test data.
Once the test cases are ready then these test cases are reviewed by peer members or team lead.
Also, the test team prepares the Requirement Traceability Matrix (RTM). RTM traces the requirements to the test cases that are needed to verify whether the requirements are fulfilled. The deliverables of this phase are Test Cases, Test Scripts, Test Data, Requirements Traceability Matrix
What I do in Test Design Phase as a Software Tester?
During the Test Design phase, I start creating test cases based on the requirements gathered. I focus on writing test cases that cover both functional and non-functional requirements. I make sure each test case includes clear steps and expected results. Besides, I also work on preparing test data and identifying the criteria for test automation if needed.
Entry Criteria: Requirements Documents (Updated version of unclear or missing requirement)
Deliverables: Test cases, Test Scripts (if automation), Test data.
In this phase, Selenium would be the most popular tool to use. However, its complexities and programming experience needed to Python or C# would definitely pose a problem to your manual QAs and automation freshers.
Here, Katalon Studio would be your go-to choice in simplifying Selenium’s essential capabilities through codeless automation, built-in keywords, and pre-defined artifact templates for test suites.
Must Read: How To Write Test Cases
4. Test Environment Setup
This phase can be started in parallel with the Test design phase.
The test environment setup is done based on the hardware and software requirement list. In some cases, the test team may not be involved in this phase. The development team or customer provides the test environment.
Meanwhile, the test team should prepare the smoke test cases to check the readiness of the given test environment.
What I do in Test Environment Setup Phase as a Software Tester?
In the Test Environment Setup phase, I ensure that the testing environment is ready for execution. This involves setting up hardware and software requirements, configuring test servers, and ensuring network settings are correctly applied. Sometimes, this phase might involve collaboration with the development or IT team to get everything in place. The goal is to mimic the production environment as closely as possible.
Entry Criteria: Test Plan, Smoke Test cases, Test Data
Deliverables: Test Environment. Smoke Test Results.
5. Test Execution
The test team starts executing the test cases based on the planned test cases. If a test case result is Pass/Fail then the same should be updated in the test cases.
The defect report should be prepared for failed test cases and should be reported to the Development Team through a bug tracking tool for fixing the defects.
Retesting will be performed once the defect was fixed. Click here to see the Bug Life Cycle.
What I do in Test Execution Phase as a Software Tester?
Once the environment is set up, I move to the Test Execution phase where I actually run the test cases. Here, I record the outcomes and compare them with the expected results. Any deviations or defects found are reported, tracked, and retested once fixed. The objective is to ensure that the software behaves as expected under different conditions.
Entry Criteria: Test Plan document, Test cases, Test data, Test Environment.
Deliverables: Test case execution report, Defect report, RTM
Must Read: How To Write An Effective Defect Report
6. Test Closure
The final stage where we prepare Test Closure Report, Test Metrics.
The testing team will be called out for a meeting to evaluate cycle completion criteria based on Test coverage, Quality, Time, Cost, Software, Business objectives.
The test team analyses the test artifacts (such as Test cases, Defect reports, etc.,) to identify strategies that have to be implemented in the future, which will help to remove process bottlenecks in the upcoming projects.
Test metrics and Test closure report will be prepared based on the above criteria.
What I do in Test Closure Phase as a Software Tester?
Finally, in the Test Closure phase, I summarize the testing process and results. This involves evaluating whether all the objectives were met and documenting any learnings or improvements for future projects. I prepare a test summary report that includes metrics, defect logs, and an overall assessment of the software quality. This phase also ensures that all test artifacts are archived for future reference.
Entry Criteria: Test Case Execution report (make sure there are no high severity defects opened), Defect report
Deliverables: Test Closure report, Test metrics
Must Read: Test Metrics
STLC Phases (Entry and Exit Criteria)
| STLC Phase | Entry Criteria | Exit Criteria | Deliverables |
|---|---|---|---|
| Requirement Analysis | Requirements specification document, Acceptance criteria document, Application architectural document | Signed off RTM, Signed off Automation feasiblity report | List of all testable requirements, Automation feasibility report (if applicable) |
| Test Planning | Requirements Documents, Automation feasbility report | Approved Test plan document, Approved Test strategy document, Signed off effort estimation document | Test Strategy, Test Plan, and Test Effort estimation document. |
| Test Design | Requirements Documents (Updated version of unclear or missing requirement), RTM, Test Plan, Test Estimation Document, Automation Analysis Report | Reviewed and approved test cases, test scripts, test data | Test cases, Test Scripts (if automation), Test data. |
| Test Environment Setup | Test Plan, Test environment setup plan, Smoke Test cases, Test Data | Working test environment setup, Valid test data setup, Successful somke test | Test Environment. Smoke Test Results. |
| Test Execution | Test Plan document, Test cases, Test Scripts, Test data, Test Environment. | Execute all planned test cases, Log all defects found | Test case execution report, Defect reports, RTM |
| Test Closure | Testing has been completed, Test Case Execution report (make sure there are no high severity defects opened) | Signed off Test Closure report | Test Closure report, Test metrics |
Advantages of STLC
- Early Detection of Defects: By testing early in the development cycle, defects can be found and fixed sooner. This helps to avoid bigger problems later on.
- Improved Quality: With systematic testing, the quality of the software improves. Each feature is checked to make sure it works as expected.
- Better Planning: Testing with clear goals and phases makes it easier to plan and track progress. Teams know what needs to be tested and when.
- Cost Savings: Finding and fixing issues early is often cheaper than doing so later in the development process. This can save money and time.
- Clear Requirements: Testing involves reviewing requirements thoroughly. This ensures that everyone understands what is needed and helps avoid misunderstandings.
- Efficient Use of Resources: Proper planning and early testing lead to a more efficient use of time and resources. Teams can focus on what is important and prioritize their tasks.
Difference between STLC vs SDLC
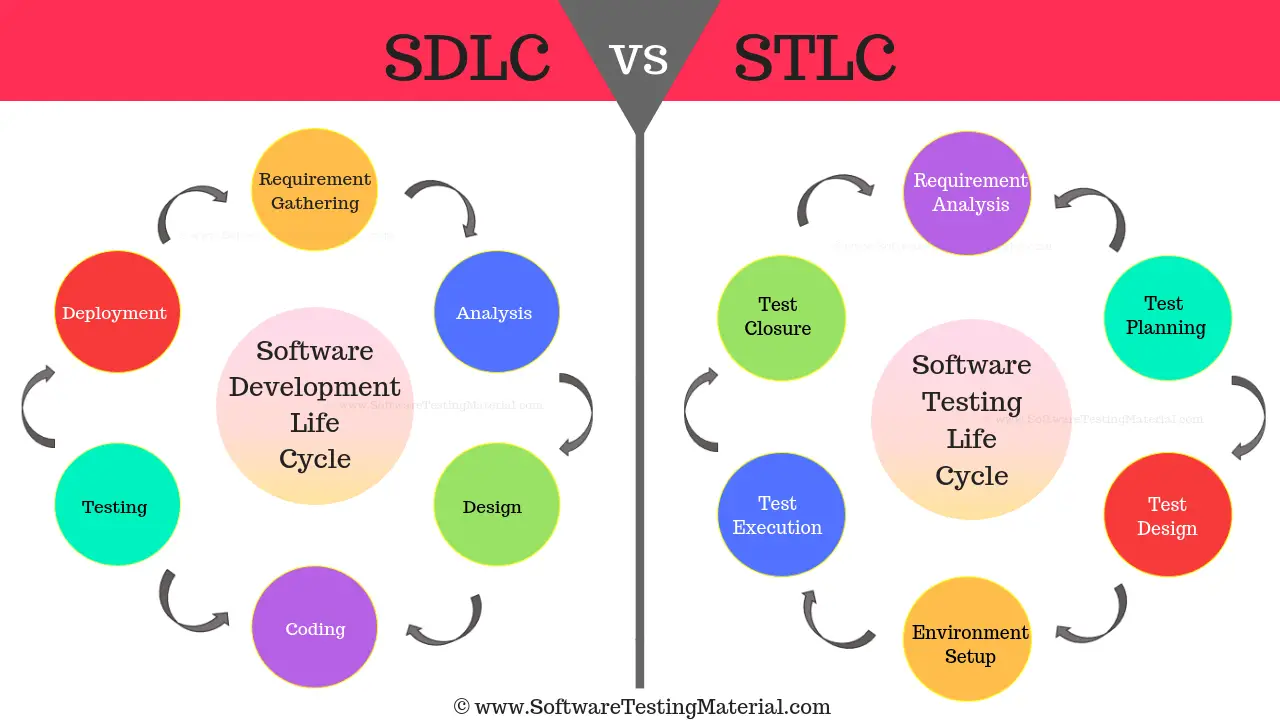
STLC and SDLC are both parts of the process of developing software, but they serve different purposes.
SDLC is the process used to plan, create, test, and deploy software. It is the overall process of software development. It starts by gathering requirements from the client or stakeholders, then moves on to design, coding, testing, and eventually deployment and maintenance of the software.
STLC, on the other hand, focuses entirely on the testing part of software development. It starts as soon as requirements are gathered, and includes phases such as test planning, designing test cases, setting up the test environment, executing tests, and finally closing the tests by evaluating the results.
The main difference is their scope. SDLC covers the whole process of creating software from start to finish, while STLC focuses just on making sure the software works properly and meets the requirements. Both are important and work together to ensure that high-quality software is delivered.
Check this detailed guide on difference between SDLC & STLC
Conclusion
Software Testing Life Cycle is a systematic way of performing testing. It gives better product quality, quick bug fixing results, and effective and efficient test results.
Like this post, please share it with your friends. If you have any questions, please comment below.
FAQs – 6 Key Phases of Testing In Software Testing
What are the 7 phases of SDLC?
The 7 Phases Of Software Development Life Cycle
Phase 1: Requirement Phase
Phase 2: Analysis Phase
Phase 3: Design Phase
Phase 4: Development Phase
Phase 5: Testing Phase
Phase 6: Deployment Phase
Phase 7: Maintenance Phase
You can read about SDLC in detail here.
What are the four phases of testing?
The four levels of software testing are crucial steps in the software testing lifecycle, ensuring that the software product is functional, reliable, and meets user expectations. These phases are: Unit Testing, Integration Testing, System Testing, and Acceptance Testing.
What are Entry and Exit Criteria in STLC?
Entry criteria are the requirements or conditions that must be met before a testing phase begins. These ensure that the necessary preparations and resources are in place. For example, all necessary test data should be available, and test environments should be set up.
Exit criteria are the conditions that must be satisfied for a testing phase to be considered complete. This ensures that testing has been thorough and the software meets quality standards. For example, all test cases should be executed, and all critical defects should be fixed.
What are the principles of STLC?
The principles of STLC are guidelines that help ensure effective and efficient testing. These principles include: Testing shows presence of defects, Exhaustive testing is impossible, Early testing, Defect clustering, Pesticide paradox, Testing is context dependent, Absence of error – fallacy. You can read in detail in this blog.
What Is the Role of Software Testing Life Cycle?
The Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC) plays a crucial role in ensuring that software is of high quality before it is released. It involves a series of systematic steps including planning, designing, executing, and evaluating tests. The main aim is to identify and fix bugs or issues early in the development process, thereby saving time and reducing costs. Through thorough testing, STLC ensures that the final product meets user requirements and functions as expected.
Related Posts:
- Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
- Bug Life Cycle (Defect Life Cycle)
- Test Metrics
- Requirement Traceability Metrics (RTM)
- Test Artifacts / Test Deliverables
- How To Write Test Strategy
- How To Write Test Plan







In test execution phase, forgot to provide a URL for bug life cycle. I think, I did static testing(review) here 🙂 Good explanation, Thank you.
and its a low severity defect
Hi Geetanjali. Thanks for pointing out. 🙂 Your inputs are welcome. Keep visiting.