What is Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), Phases, SDLC vs STLC
In this Software Development Life Cycle tutorial, we are going to discuss the following
In this post, we’ll take you through everything you need to know about the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). In the earlier post, we have learned what is Software Testing and Software Testing Life Cycle.
We’ll start with a Definition of SDLC, SDLC Phases, and the following.
What is SDLC?
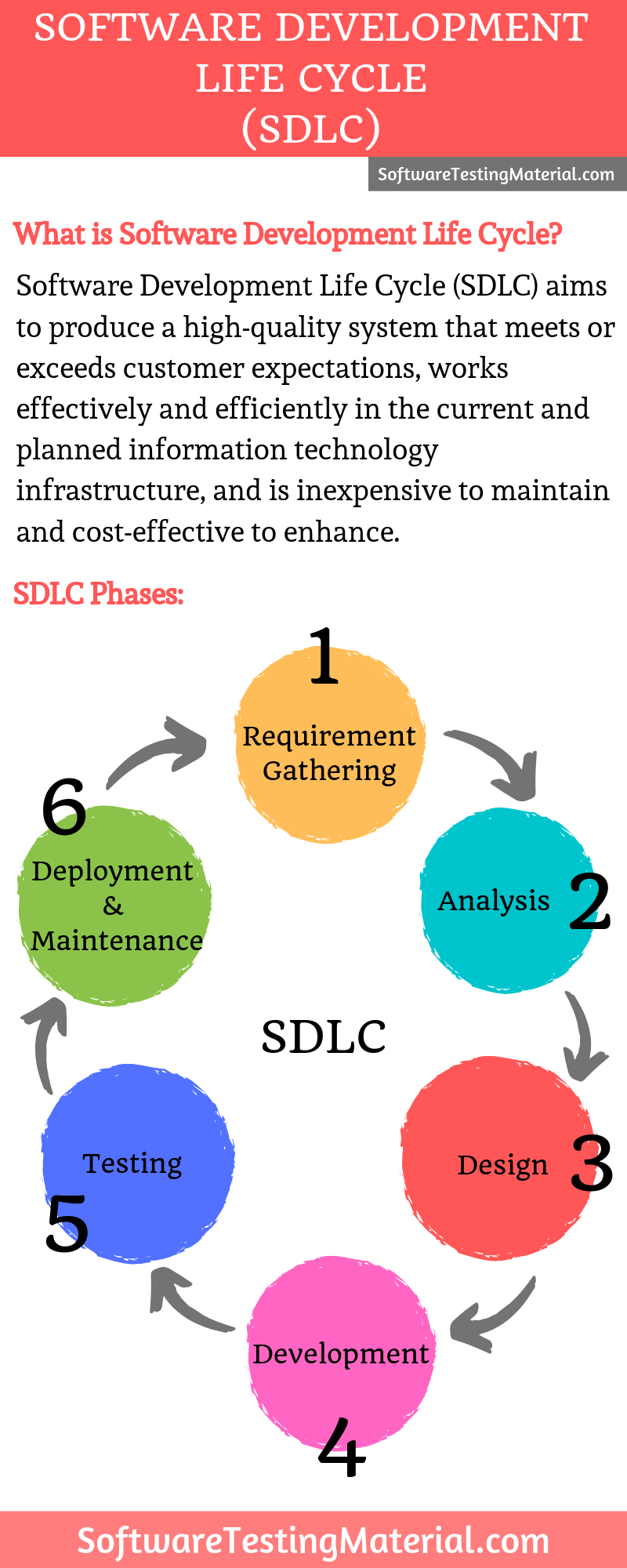
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) aims to produce a high-quality system that meets or exceeds customer expectations, works effectively and efficiently in the current and planned information technology infrastructure, and is inexpensive to maintain and cost-effective to enhance.
Detailed Explanation (What is SDLC)
A process followed in software projects is SDLC. Each phase of SDLC produces deliverables required by the next phase in the life cycle. Requirements are translated into design. Code is produced according to the design. Testing should be done on a developed product based on the requirement. The deployment should be done once the testing was completed. It aims to produce a high-quality system that meets or exceeds customer expectations, works effectively and efficiently in the current and planned information technology infrastructure, and is inexpensive to maintain and cost-effective to enhance.
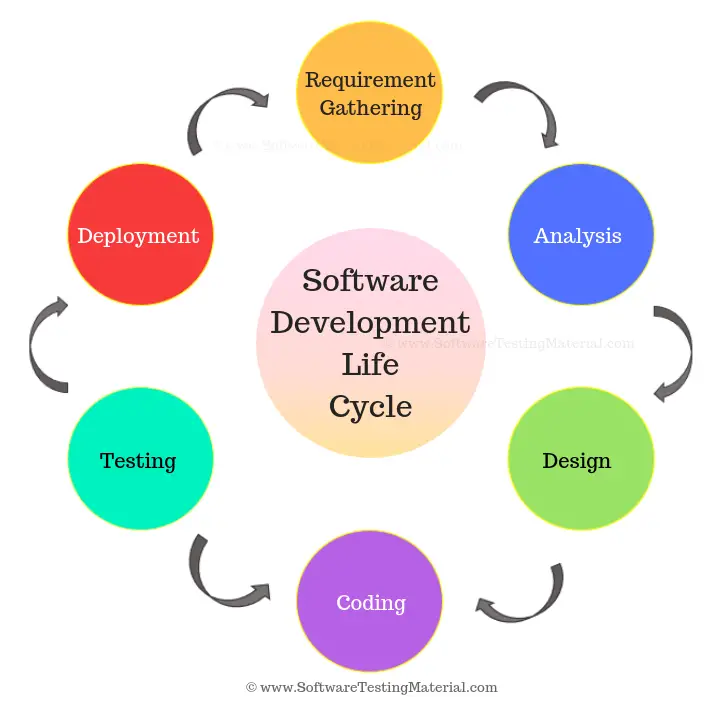
What is SDLC Process
SDLC is a process which follows in Software Projects to develop a product in a systematic way and to deliver a high-quality product. By following proper SDLC process, Software companies can react well to the market pressure and release high-quality software. This process involves different stages of SDLC right from the requirement stage to deployment and maintenance phase. These SDLC phases we will see later section of this post.
Why SDLC
Some of the reasons why SDLC is important in Software Development are as follows.
- It provides visibility of a project plan to all the involved stakeholders
- It helps us to avoid project risks
- It allows us to track and control the project
- It doesn’t conclude until all the requirements have been achieved
Don’t miss: Difference between SDLC & STLC (SDLC Vs STLC)
What are the 7 Phases of SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle Phases)
Seven Phases of Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC Phases) are as following:
- Phase 1: Requirement Phase
- Phase 2: Analysis Phase
- Phase 3: Design Phase
- Phase 4: Development Phase
- Phase 5: Testing Phase
- Phase 6: Deployment And Maintenance Phase
Check out the below video to watch “Software Development Life Cycle Phases (SDLC Phases)”
Please be patient. The video will load in some time.
#1. Requirement Phase
Requirement gathering and analysis is the most important phase in the software development lifecycle. Requirement phase is the first step of the SDLC. Business Analyst collects the requirement from the Customer/Client as per the clients business needs and documents the requirements in the Business Requirement Specification (document name varies depends upon the Organization. Some examples are Customer Requirement Specification (CRS), Business Specification (BS), etc., and provides the same to Development Team.
#2. Analysis Phase
Once the requirement gathering and analysis is done the next step is to define and document the product requirements and get them approved by the customer. This is done through the SRS (Software Requirement Specification) document. SRS consists of all the product requirements to be designed and developed during the project life cycle. Key people involved in this phase are Project Manager, Business Analyst and Senior members of the Team. The outcome of this phase is the Software Requirement Specification.
#3. Design Phase
It has two steps:
HLD – High-Level Design – It gives the architecture of the software product to be developed and is done by architects and senior developers
LLD – Low-Level Design – It is done by senior developers. It describes how each and every feature in the product should work and how every component should work. Here, only the design will be there and not the code
The outcome from this phase is High-Level Document and Low-Level Document which works as an input to the next phase
#4. Development Phase
Developers of all levels (seniors, juniors, freshers) involved in this phase. This is the phase where we start building the software and start writing the code for the product. The outcome from this phase is Source Code Document (SCD) and the developed product.
#5. Testing Phase
When the software is ready, it is sent to the testing department where Test team tests it thoroughly for different defects. They either test the software manually or using automated testing tools depends on the process defined in STLC (Software Testing Life Cycle) and ensure that each and every component of the software works fine. Once the QA makes sure that the software is error-free, it goes to the next stage, which is Implementation. The outcome of this phase is the Quality Product and the Testing Artifacts.
#6. Deployment & Maintenance Phase
After successful testing, the product is delivered/deployed to the customer for their use. Deployment is done by the Deployment/Implementation engineers. Once when the customers start using the developed system then the actual problems will come up and needs to be solved from time to time. Fixing the issues found by the customer comes in the maintenance phase. 100% testing is not possible – because, the way testers test the product is different from the way customers use the product. Maintenance should be done as per SLA (Service Level Agreement)
Types of Software Development Life Cycle Models
There are various Software Development Life Cycle models in the industry which are followed during the software development process. These models are also referred to as Software Development Process Models.
Each SDLC model might have a different approach but the Software Development Phases and activities remain the same in all the models.
Some of the Software Development LifeCycle Models (SDLC Models) followed in the industry are as follows:
Waterfall Model
Waterfall Model is a traditional model. It is aka Sequential Design Process, often used in SDLC, in which the progress is seen as flowing downwards like a waterfall, through the different phases such as Requirement Gathering, Feasibility Study/Analysis, Design, Coding, Testing, Installation, and Maintenance. Every next phase is begun only once the goal of the previous phase is completed. This methodology is preferred in projects where quality is more important as compared to schedule or cost. This methodology is best suitable for short term projects where the requirements will not change. (E.g. Calculator, Attendance Management) Learn in detail – Waterfall Model
Spiral
The spiral model works in an iterative nature. It is a combination of both the Prototype development process and the Linear development process (waterfall model). This model places more emphasis on risk analysis. Mostly this model adapts to large and complicated projects where risk is high. Every Iteration starts with planning and ends with the product evaluation by the client. Learn in detail – Spiral
V Model
V-model is also known as the Verification and Validation (V&V) model. In this, each phase of SDLC must be completed before the next phase starts. It follows a sequential design process same as the waterfall model. Learn in detail – V Model
Prototype
The Prototype Model is one of the most used Software Development Life Cycle Models (SDLC models). A prototype of the end product is first developed prior to the actual product. Usually, this SDLC model is used when the customers don’t know the project requirements beforehand. By developing the prototype of the end product, it gives the customers an opportunity to see the product early in the life cycle.
It starts by getting the inputs (requirements) from the customers and undergoes developing the prototype. By getting the customer’s feedback, requirements are refined. Actual product development starts once the customer approves the prototype. The developed product is released for customer’s feedback. Released product is refined as per the customers. This process goes on until the model is accepted by the customer.
Agile SDLC
Agile Scrum Methodology is one of the popular Agile software development methods. There are some other Agile software development methods but the popular one which is using widely is Agile Scrum Methodology. The Agile Scrum Methodology is a combination of both Incremental and Iterative model for managing product development. Learn in detail – Agile
The other related SDLC Methodologies are Rapid Application Development, Rational Unified Model, Hybrid Model, etc.,
SDLC Interview Questions
Some of the questions you may face in the Software Testing interview related to the Software Development Life Cycle are as follows. For answers check this Manual Testing Interview Questions post
1. What is SDLC?
2. What is the difference between SDLC and STLC?
3. What are the different types of SDLC models?
4. What are the different phases of the Waterfall model?
5. What are the drawbacks of the Waterfall model?
6. What are LLDs and HLDs in SDLC?
7. What is a V-model in SDLC & mention its benefits?
8. What is an Agile model & mention its benefits?
9. What do you understand by the waterfall model?
10. What is the Requirement phase in SDLC?
11. What is the Analysis phase?
12. What is the Design phase?
13. What is the Testing phase?
14. What is the Deployment & Maintenance phase?
Get this free Software Testing Interview Questions eBook
SDLC Infographics
Related Posts:
- Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC)
- Bug Life Cycle (Defect Life Cycle)
- Test Metrics
- Requirement Traceability Metrics (RTM)
- Test Artifacts / Test Deliverables
- How To Write Test Strategy
- How To Write a Test Plan







Very nice n easily understanding. ..
Thanks Savita Babar. Keep visiting.
Hi sir please check for 7 principal of software testing this page is not working showing error page kindly go through this and kindly fix it for us …
Hi Shitu,
Please check this link.
thanks..its explanation is with very easy words…so easy to understand.
Thanks Shraddha
Thank you Rajkumar for your article. It is easy & clear like water to understand the SDLC.
Welcome Ahmed. If you have any queries, let us know.
Very nice and neat article. Thanks!