What is a Datacenter Proxy | Everything You Should Know
So, what exactly is a datacenter proxy, and why should you care? In the simplest terms, datacenter proxies are IP addresses that originate from a secondary corporation and have no connection to your internet service provider (ISP). They are instrumental in providing anonymity, enabling high-speed data extraction, and promoting business scalability.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a business owner seeking to protect your digital assets, or someone interested in efficient web scraping, understanding datacenter proxies can offer you significant advantages.
This blog post aims to break down the complexities surrounding datacenter proxies, ensuring you have the key information needed to navigate the digital landscape of today’s world. Let’s dive in.
What are datacenter proxies?
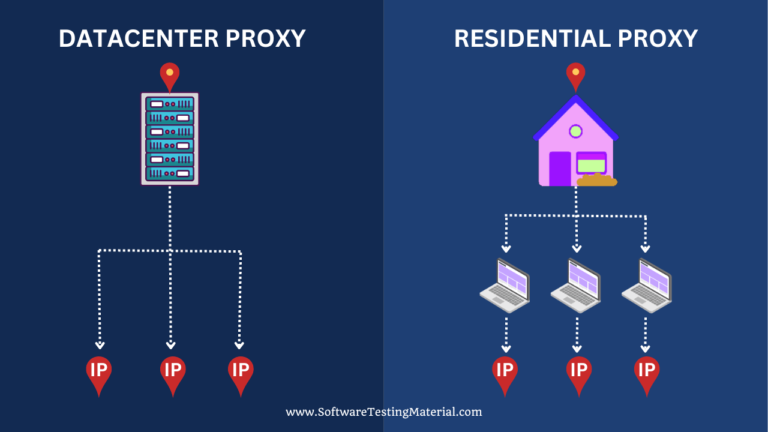
Datacenter proxies (aka DC proxies) are a type of proxy server that is hosted by a datacenter rather than an internet service provider (ISP) or an organization’s own infrastructure. These types of proxies act as intermediaries between the user and the internet, allowing users to access websites and online services without revealing their IP address.
Read more: Datacenter Proxies vs Residential Proxies
How do datacenter proxies work?
Datacenter proxies work by routing the user’s request through a datacenter server before connecting to the website or online service. This means that the user’s IP address is masked by the datacenter proxy’s IP address, providing anonymity and hiding the user’s true location.
Why are datacenter proxies popular?
Datacenter proxies are popular for several reasons. Firstly, they offer high levels of anonymity and security as the user’s IP address is hidden. This is particularly useful for individuals and businesses that want to protect their online activities and information from being tracked or monitored.
Secondly, datacenter proxies are typically faster than other types of proxies such as residential proxies which are hosted by ISPs. This is because datacenter servers are specifically designed for high-speed internet connections and can handle a larger volume of requests.
Finally, datacenter proxies are more affordable than other types of proxies, making them a cost-effective option for businesses and individuals who require large quantities of proxies for various online activities such as web scraping or ad verification.
Common uses for datacenter proxies
Datacenter proxies have a wide range of use cases. Some common examples include:
- Web scraping: Datacenter proxies are often used for web scraping as they provide fast, anonymous and cost-effective access to large amounts of data from various websites.
- Ad verification: Advertisers use datacenter proxies to verify the placement and performance of their online ads without being detected by competitors.
- SEO monitoring: Search engine optimization (SEO) professionals use datacenter proxies to monitor search engine rankings and track keyword changes.
- Sneaker copping: Datacenter proxies are popular in the sneaker copping community as they allow users to purchase limited edition sneakers from multiple locations without being detected by retail websites.
- Social media management: Datacenter proxies enable social media managers to create and manage multiple accounts on platforms like Instagram, Twitter or Facebook without being flagged for suspicious activity.
The downsides of datacenter proxies
While datacenter proxies offer many benefits, there are also some downsides to consider. These include:
- Location restrictions: Datacenter proxies are not attached to a physical location like residential or mobile proxies, so they cannot be used for geo-targeting purposes.
- Not suitable for sensitive tasks: Due to their lack of real-world associations, datacenter proxies are not recommended for tasks that require high levels of security, such as online banking or financial transactions.
- Blacklisting: Some websites have measures in place to detect and block datacenter proxy traffic, which can lead to restricted access or even blacklisting of the proxy IPs.
- Limited rotation options: Unlike residential or mobile proxies, datacenter proxies do not rotate frequently, making them more easily traceable and detectable by websites.
- Lower success rates: As datacenter proxies are often used by multiple users at once, there is a higher chance of encountering errors or delays in connection compared to dedicated residential or mobile proxies.
FAQ’s
What are the alternatives to datacenter proxies?
Residential proxies, an alternative to datacenter proxies, use real IP addresses from ISPs, making them difficult to detect. They are ideal for web scraping secure websites and collecting identity-sensitive public information. Common use cases include review monitoring, travel fare aggregation, ad verification, and anti-phishing.
How to configure datacenter proxies?
To configure proxies, input the IP, port, and credentials (username and password) provided by your proxy provider into your preferred tool. Verify the configuration’s success by visiting an IP-checking website.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Datacenter proxies offer a cost-effective and efficient solution for various online tasks, from ad verification to social media management. However, they are not without their limitations and may not be suitable for certain use cases. It is important to weigh the pros and cons when considering using datacenter proxies and choose the right type of proxy for your specific needs. With proper usage, datacenter proxies can provide a reliable and effective means of connecting to the internet anonymously.
Related posts:
- Best HTTP And HTTPS Proxies List
- Best Residential Proxy Server Service
- Best Online Proxy Websites List
- Best Proxy Server List
- Best VPN Services
- What is a Proxy Server
- Proxy vs VPN: What is the Difference