PDCA Cycle | A Detailed Guide on Plan Do Check Act Cycle
What is PDCA Cycle?
The Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle is an iterative four-step management method used in business to focus on continuous improvement of processes, products, or services and to resolve problems.
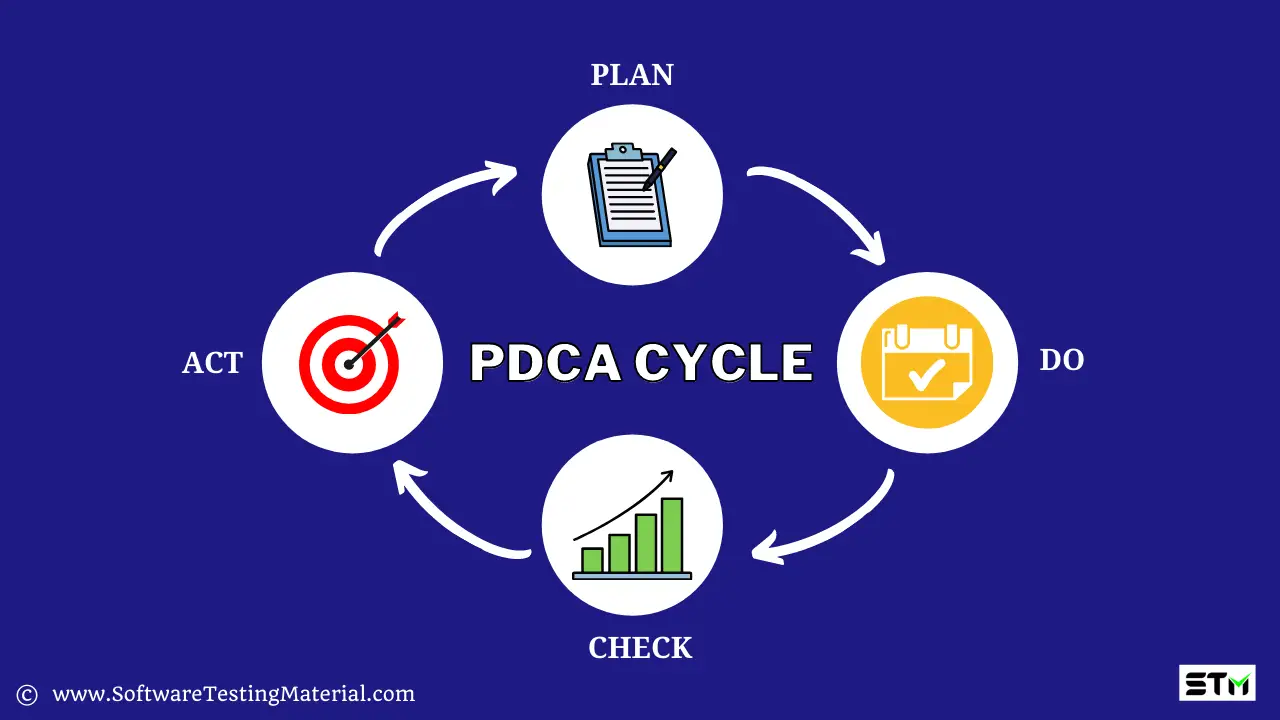
The PDCA cycle consists of four steps namely Plan, Do, Check, and Act. It is one of the key concepts of quality.
The concept of the PDCA cycle was developed by Dr. William Edwards Deming in the 1950s as a learning or improvement process.
Dr. William Edwards Deming is considered by many as the Total Quality Management (TQM) guru.
Deming created this concept based on an idea from his mentor American physicist Walter A. Shewhart and he himself called it as Shewhart Cycle.
PDCA Cycle is also called the following
- PDSA Cycle (Plan Do Study Act)
- PDCA Cycle (Plan Do Check Adjust)
- Deming Cycle/Deming Circle/Deming Wheel
- Shewhart Cycle
In simple words, we can say PDCA is used to solve the problems and improve the process.
Solve the problems – If something is not functioning properly. We use PDCA as an analysis tool to uncover the hidden problems and find solutions.
Improve the process – If something which is functioning not giving results at its best. We use PDCA as an analysis tool to find potential improvements to existing function.
When To Use PDCA Cycle?
It can be used in all types of organizations and works well to implement Total Quality Management or Six Sigma initiatives.
Some of the cases where we use the PDCA Cycle are
- When a new improvement project starts
- When implementing any changes
- When defining a repetitive process
It is also used by companies who follow the Kaizen method. Kaizen method is an organizational mindset that focuses on small, frequent changes that result in major improvements over time.
How the PDCA Cycle Works
Let’s see what we do in each stage of the PDCA Cycle in SDLC.
You could also check this video
PLAN:
Recognize an opportunity (either a problem or an improvement). Plan a change (either to solve a problem or to improve some areas) and decide what goal to achieve.
Here we define the objective, strategy, and supporting methods to achieve the goal of our plan.
DO:
To design or revise the business requirement as planned
Here we implement the plan (in terms of putting the plan into action) and test its performance
CHECK:
Evaluate the results to make sure whether we reach the goals as planned
Here we make a checklist to record what went well and what did not work (lessons learned)
ACT:
If the changes are not as planned then continue the cycle to achieve the goal with a different plan.
Here we take action on what is not working as planned. The task is to keep trying to improve the process with a different plan.
PDCA Cycle is a continuous process until we achieve the goals that we planned.
Pros and cons of PDSA Cycle
The advantages and disadvantages of PDCA cycle are
Advantages:
The benefits of PDCA cycle are as follows.
- Simple to understand and powerful when implementing
- It can be applied to any type of organization
- Helps in problem solving and process improvement
Disadvantages:
- It makes the process slow so it is not a recommended approach when you are dealing with an urgent problem.
- It is a continuous process rather than an end-to-end process. So it requires committed leadership.