How To Perform QR Code Testing | QR Code Testing Guide
QR Codes have become a common way to share information quickly and easily, from accessing websites to making payments. For software testers, understanding how to test QR Codes is essential to ensure they work as expected. QR Code testing helps verify that the codes function properly on different devices and with various scanning apps, reducing errors and improving user satisfaction.
Without thorough QR Code testing, users may face broken links or incorrect information, which can lead to frustration and loss of trust. This makes QR Code testing a critical part of delivering quality digital experiences.
In this article, we will learn what is QR code, how to test QR codes and the following.
What is a QR Code?
A QR Code, short for Quick Response Code, is a type of two-dimensional barcode that can store information. It is commonly used to share links, text, or other data that can be read quickly by a smartphone or scanner. QR Codes are made up of black and white patterns and can store much more information than traditional barcodes. They are widely used because they are fast, easy to scan, and practical for many applications, such as accessing websites, making payments, or sharing contact details.
Types of QR Codes
There are two main types of QR Codes, each designed for specific purposes and levels of complexity. Here are some of the main types:
#1. Static QR Codes
Static QR Codes are fixed, meaning the information they contain cannot be changed once they are created. They are best suited for simple, unchanging data like plain text, a single URL, or contact details. For example, a business might use a static QR Code on a product label to direct customers to a website.
#2. Dynamic QR Codes
Unlike static QR Codes, dynamic QR Codes can be edited or updated after they are created. This makes them more flexible and ideal for situations where the data may change over time, such as promotional campaigns or temporary event details. They can also track scan statistics, like the number of scans or locations.
QR Code Vs Bar Code
| Feature | QR Code | Bar Code |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Square-shaped with a grid pattern | Rectangular lines of varying thickness |
| Data Capacity | Can store large amounts of data, including text, URLs, and multimedia | Limited to numeric or alphanumeric data |
| Scan Directions | Can be scanned from any angle (360 degrees) | Requires specific alignment to scan |
| Storage Type | Stores data both vertically and horizontally | Stores data in a single dimension (horizontally) |
| Speed | Faster scanning due to multidimensional data storage | Slower scanning due to one-dimensional data |
| Durability | Can withstand damage and still function if partially ruined | Does not work if damaged significantly |
| Usage | Commonly used in marketing, digital payments, and modern apps | Commonly used in packaging, inventory, and retail |
| Design | Allows customization with logos and colors | Typically cannot be customized visually |
| Technology Used | Advanced technology for encoding large and complex data | Simpler technology for basic data encoding |
| Evolution | Advanced and newer compared to Bar Codes | Older and traditional coding system |
Benefits of Using a QR Code
Whether for business, marketing, or personal convenience, QR Codes offer following benefits.
- Quick and Easy to Use: QR Codes can be scanned in seconds using a smartphone camera, making them very convenient.
- Can Store a Lot of Information: They can hold more data than traditional barcodes, such as website links, text, or even payment details.
- Versatile Applications: QR Codes can be used for many purposes, like accessing menus, sharing contact information, or making online payments.
- Contactless and Safe: Especially during times when hygiene is important, QR Codes allow users to access information without physical contact.
- Cost-Effective: They are simple to create and require no special equipment, reducing costs for businesses and individuals.
- Easy to Share: QR Codes can be printed on materials like flyers, posters, or business cards to quickly share information.
How to Test QR Codes
Testing QR codes is a straightforward process. Follow these steps to ensure the QR code is working correctly:
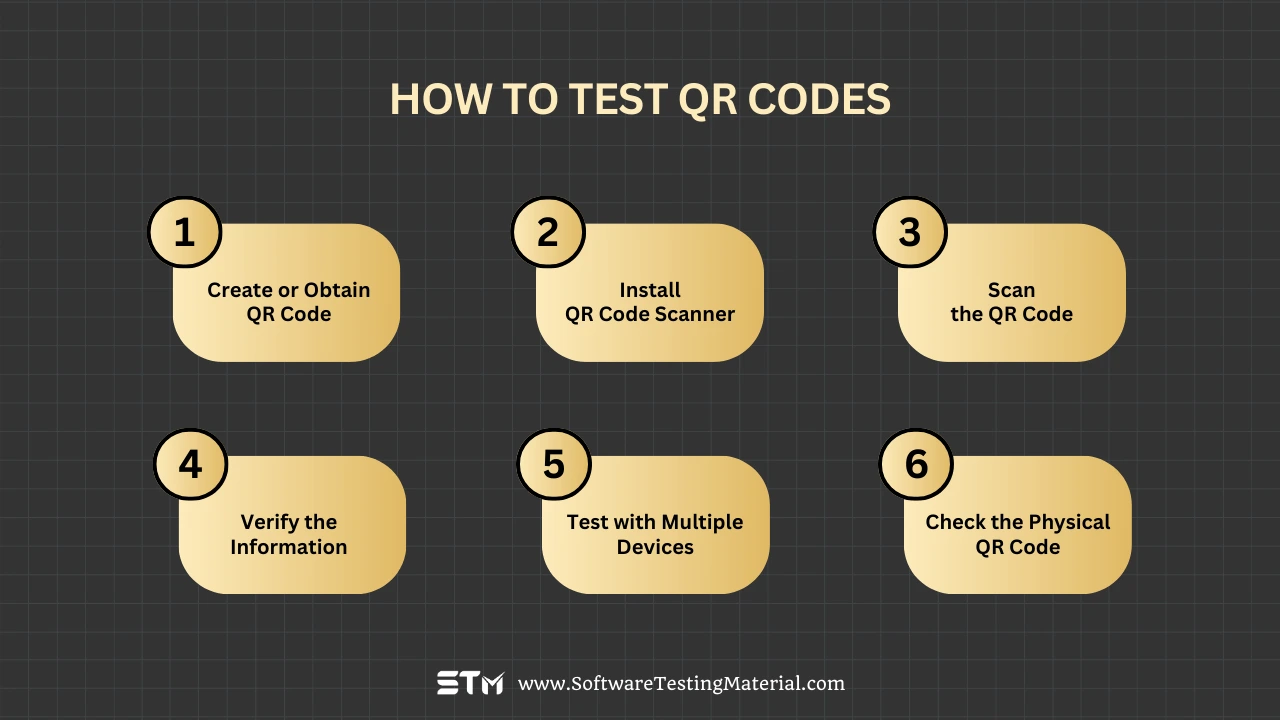
Step 1: Create or Obtain the QR Code
If you are creating a QR code, use a QR code generator to produce one. Double-check that all the data or links included in the QR code are accurate.
Step 2: Install a QR Code Scanner
Most modern smartphones and tablets have built-in QR code scanning features, usually accessible through the device’s camera app. If your device does not support QR scanning natively, download a trusted QR code scanner application from your device’s app store.
Step 3: Scan the QR Code
Open your camera app or QR scanner app, and point your device’s camera directly at the QR code. Ensure the QR code fits within the frame or guidelines provided by the app. Hold your device steady for a few seconds as the scanner detects the code.
Step 4: Verify the Information
Once the QR code is scanned, it will typically display the data or redirect to a link. Check that the information or link corresponds to the intended purpose of the QR code. For instance, if the code is supposed to take you to a website, ensure the correct website opens.
Step 5: Test with Multiple Devices
QR codes should be accessible on most devices, so try scanning the code with different smartphones or tablets to confirm compatibility. This helps identify any potential issues with specific devices.
Step 6: Check the Physical QR Code
If the QR code is printed on materials like brochures or posters, test it in various lighting conditions and from different distances. Ensure that the QR code can be scanned easily without distortion.
By following these steps, you can confidently ensure that QR codes are functional, accessible, and ready for use.
How to Check If a QR Code Works
#1. Scan the QR Code with a Smartphone
Use the camera on your smartphone to scan the QR code. Most modern smartphones can recognize QR codes directly through their default camera app. Hold your device steady and make sure the entire QR code fits within the frame. If the camera does not recognize the code, test it using a QR code reader app from the app store.
#2. Verify the Target Link or Action
Once you scan the QR code, it should direct you to the intended link or app, or perform the expected action, such as opening a webpage or downloading a file. Ensure the result matches what you expect. If the link is incorrect or leads to an error, you may need to review the QR code’s design or content.
#3. Test Different Devices
Test the QR code on various devices, including smartphones and tablets from different manufacturers. Not all devices work the same way, so testing on multiple devices ensures broader compatibility for your audience.
#4. Check the Internet Connection
If the QR code requires an internet connection to access content, make sure your device is connected to Wi-Fi or cellular data. A poor or nonexistent internet connection may cause the QR code to seem like it doesn’t work, even if it is functional.
#5. Inspect the QR Code Design
If the QR code includes custom designs, such as colors or logos, make sure these modifications do not interfere with its scannability. Avoid making the code too small or using colors with low contrast, as these factors can make scanning difficult.
#6. Review the Placement of the QR Code
If the QR code is displayed on physical materials, such as posters or signs, ensure it is placed at an accessible height and is not distorted. Additionally, check that it is free from glare, shadows, or other obstructions that may affect scanning.
By carefully following these steps, you can confirm that your QR code works smoothly and is ready for its intended use. Ensuring functionality beforehand helps avoid issues and improves the user experience.
Best Practices when Generating Your Sample QR Codes to Scan More Accurately
#1. Choose the Right Contrast and Color
Always ensure there is a strong contrast between the QR code and its background. Use dark-colored codes (e.g., black or dark blue) on a light-colored background (e.g., white). Avoid using low-contrast combinations or multi-colored designs as they might confuse scanners.
#2. Maintain the QR Code Size
The size of the QR code matters greatly for its scannability. Make sure the QR code is neither too small nor too large. A minimum size of 1 x 1 inch (2.5 x 2.5 cm) is recommended for most uses, but larger codes are preferable for broader visibility, especially in print materials.
#3. Avoid Overcrowding with Data
The more information you store in the QR code, the denser and more complex it becomes. Keep the encoded information simple and concise, like URLs or short text, to ensure fast and accurate scanning.
#4. Provide Quiet Zones Around your QR Code
Include a margin or “quiet zone” around the QR code. This blank space helps scanners detect the boundaries of the code. The margin should ideally be four times the width of the code’s smallest data module (the squares in the code).
#5. Use High-Quality Resolution
For printed materials or digital displays, ensure your QR code is in high resolution. Pixelated or blurry codes can lead to scanning errors or failures. Export the code in a high-resolution file format, such as PNG or SVG.
#6. Test Across Multiple Devices and Apps
Before finalizing your QR code, test it using different devices (smartphones, tablets) and scanning apps. This ensures compatibility and smooth scanning for all users.
#7. Optimize for Usage Conditions
Think about where your QR code will be used. If it will be displayed outdoors, ensure it is resistant to weather and lighting conditions. For digital media, ensure it is large enough to be visible on various screen sizes.
#8. Check Internet Connectivity
If your QR code links to an online resource, ensure the destination URL or page is live and easy to load. Slow or inactive links can frustrate users and reduce the effectiveness of your QR code.
By keeping these best practices in mind, you can create accurate, user-friendly sample QR codes that ensure a seamless scanning experience.
Common QR Code Testing Mistakes to Avoid
#1. Not Testing on Different Devices
One of the biggest mistakes is only testing QR codes on a single device. Different smartphones, operating systems, or QR code scanning apps may behave differently. Some older devices might struggle to scan certain QR codes, so it’s important to test the code on a variety of devices to ensure compatibility.
#2. Ignoring Lighting Conditions
Testing a QR code only in perfect lighting can lead to issues when users attempt to scan it in other conditions. For example, dimly lit environments or excessively bright lights can make scanning harder. Always test your QR code in multiple lighting settings, including low light, artificial light, and sunlight.
#3. Using Poor-Quality Prints
QR codes that are printed at a low resolution or on reflective materials can become harder to scan. Always check that the printed version of the QR code is sharp and clear. Avoid glossy paper or surfaces that can create glare, which might confuse the scanner.
#4. Testing at Only One Size
QR codes that are too small or too large might not work effectively. If the size is too small, some cameras may have difficulty focusing on the code. If it’s too large, it may distort the code during display. Check your QR code at all planned sizes, whether for small business cards or large posters.
#5. Overlooking Scanning Distance
Placing a QR code where it’s either too far to scan or too close to fit within the camera’s view can cause user frustration. Always test the scanning distance for your QR code to make sure it’s practical for its intended use, such as a poster at eye level or a code on a product package.
#6. Not Verifying the Destination URL
A common mistake is linking a QR code to a broken or outdated URL. Always check the destination link to make sure it is live, loading quickly, and is still relevant. Additionally, avoid using URLs that are excessively long or prone to errors, as they can lead to scanning and redirection issues.
#7. Forgetting to Test Print and Digital Versions
Sometimes QR codes look perfect on a screen but fail to scan when printed, and vice versa. Ensure you test both the digital and printed versions of the QR code to guarantee they function correctly and maintain readability in both formats.
By avoiding these mistakes, you can ensure that your QR codes work effectively and provide users with a smooth and frustration-free scanning experience. Testing thoroughly and in different conditions is the key to creating user-friendly QR codes.
Testing QR Code Online Using Camera Image Injection
Testing a QR code online using camera image injection is a helpful way to check if your code works correctly without needing to print it out. This process involves simulating a QR code scan directly on your computer using special tools or software. Here are the steps to perform this test:
#1. Choose Image Injection Software
First, you need software or an emulator that allows camera image injection. Examples include Android Studio or specific QR code testing apps available online.
#2. Upload the QR Code Image
Save your QR code as an image file (like PNG or JPG) on your device. Then, upload this image to the image injection program or emulator. This step simulates the camera’s action of “seeing” the QR code.
#3. Simulate the Scan
Use the software to simulate scanning the QR code. The program will read the uploaded image just like a camera would when scanning a physical QR code.
#4. Check the Results
Analyze the output to ensure the QR code redirects to the correct website, displays the right data, or performs the action it was designed for. Make sure to test multiple times to confirm accuracy.
#5. Fix Errors if Needed
If the code does not work as expected, check for mistakes like incorrect URLs, blurry images, or improper QR code size. Adjust the design and retest until it works perfectly.
By following these steps, you can test your QR code quickly and efficiently online, avoiding the need for physical testing during the initial stages. This ensures your QR code is fully functional before sharing it with others.
Sample Test Cases for QR Code Testing
Test Case 1: Verify QR Code Scans Correctly
Objective: Ensure the QR code is scannable and processes correctly.
Steps:
- Open a QR code scanner app on your smartphone or device.
- Point your device’s camera at the QR code.
- Check if the app successfully detects and scans the QR code.
- Verify that it links to the intended website or displays the intended content.
Expected Result: The QR code scanner detects the QR code without issues and opens the correct link or displays the intended information.
Test Case 2: Test Scanning from Varying Angles
Objective: Confirm the QR code can be scanned from different angles.
Steps:
- Open your QR code scanner app on your device.
- Hold the scanner at various angles (e.g., straight, tilted left, tilted right) while scanning the QR code.
- Verify if the scanner still detects the QR code and processes it appropriately.
Expected Result: The QR code is scannable from multiple angles without any distortion or scanning error.
Test Case 3: Test Scanning from Different Distances
Objective: Verify the QR code can be scanned at various distances.
Steps:
- Open the QR code scanner app on your device.
- Scan the QR code while holding your device at close, medium, and far distances from the QR code.
- Note whether the scanner detects the code properly at each distance.
Expected Result: The QR code works from all practical scanning distances.
Test Case 4: Test Scanning on Different Devices
Objective: Ensure compatibility across various devices and scanners.
Steps:
- Use a variety of devices (e.g., smartphones, tablets, dedicated QR code scanners).
- Scan the same QR code with each device.
- Verify whether all devices can scan the code and display the correct information.
Expected Result: The QR code functions seamlessly across all tested devices.
Test Case 5: Validate Functionality with a Screenshot
Objective: Confirm the QR code works when scanned from a digital screenshot.
Steps:
- Take a screenshot of the QR code.
- Open the screenshot on a device.
- Use another device to scan the QR code from the screenshot.
Expected Result: The QR code is scannable from the screenshot and opens the intended link or content.
Test Case 6: Check QR Code Under Poor Lighting
Objective: Ensure the QR code can be scanned in low-light conditions.
Steps:
- Dim the lighting around the QR code.
- Scan the QR code using your QR code scanner app.
- Verify whether it works despite the reduced lighting.
Expected Result: The QR code remains functional even in dim lighting, though scanning might take slightly longer.
Test Case 7: Verify QR Code After Printing
Objective: Confirm the QR code’s functionality after being printed.
Steps:
- Print the QR code onto paper or other materials.
- Use your QR code scanner app to scan the printed QR code.
- Check if the scanner detects the code and follows the link or displays content correctly.
Expected Result: The QR code works flawlessly after being printed and links to the desired information.
Test Case 8: Check QR Code for Damage Effects
Objective: Examine the effect of minor damage or wear on QR code functionality.
Steps:
- Slightly smudge or scratch the QR code (without completely destroying its pattern).
- Use a QR code scanner to scan the damaged QR code.
- See if it can still scan and process correctly.
Expected Result: The QR code should still scan if the damage does not affect critical areas of the pattern.
Test Case 9: Confirm Content Accuracy
Objective: Validate that the QR code links to the correct and updated information.
Steps:
- Scan the QR code using a QR code scanner app.
- Check if the content (e.g., website, text, or image) is accurate and reflects what was intended.
Expected Result: The QR code leads to the correct content without errors or outdated links.
Testing your QR codes with these sample cases ensures consistent functionality and reliability across various conditions and devices. Regular testing is essential to maintain user trust and satisfaction.
QR Code Test Automation Tools
Using QR code test automation tools can simplify the process of ensuring your QR codes work efficiently. Here are some popular QR code test automation tools and their overview.
#1. Testrigor
Testrigor is a powerful automation tool that allows you to test QR codes effortlessly. It uses plain English commands, making it easy to create and run automated test cases without technical expertise. Testrigor can simulate scanning QR codes across different devices and capture results to confirm they work correctly. Its simplicity and support for various platforms make it a great choice for QR code testing.
#2. HeadSpin
HeadSpin offers a robust infrastructure for testing QR codes on real devices. It helps ensure compatibility across multiple device types and operating systems. With HeadSpin, you can run performance and functionality tests to verify that the QR code leads to the correct destination without errors. It’s especially useful for larger teams looking for detailed analytics and insights about their QR code’s behavior.
#3. BrowserStack
BrowserStack is another versatile tool for testing QR codes. It provides access to a wide range of devices and browsers, allowing you to test your QR code in different environments. BrowserStack also lets you upload your QR code and simulate user interactions to test its functionality, ensuring it works perfectly across various platforms. Its cloud-based interface makes it convenient for collaborative testing.
By using these tools, you can ensure that your QR codes are reliable, functional, and ready to use across different devices and scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Know if a QR Code Is Legit?
To know if a QR code is legit, check the source before scanning it. Only scan codes from trusted websites, businesses, or people you know. Avoid scanning codes from unknown sources, especially in public places. If the code asks for personal information or leads to a suspicious website, do not proceed. Use a secure QR scanner app that warns you about unsafe links.
How Do I Test a QR Code With My Phone?
To test a QR code with your phone, open your camera app and point it at the QR code. Make sure the code is clear and steady in the frame. If your phone supports QR scanning, a link or notification will pop up. Tap it to see where the QR code leads. If it doesn’t work, you can try using a QR code scanning app.
Can a QR Code Be Scanned if It Was Damaged?
Yes, a QR code can still be scanned if it is slightly damaged. QR codes are designed with error correction, which means they can sometimes work even if parts of the code are missing or obscured. However, if the damage is too severe, the code may not scan properly. It’s best to keep QR codes clean and undamaged for reliable use.
Will a Screenshot of a QR Code Still Work?
Yes, a screenshot of a QR code will still work as long as the image is clear and nothing is distorted. You can scan the QR code from the screenshot using your phone or another device, just like you would with a printed QR code.
How frequently should I test my QR codes?
You should test your QR codes regularly to make sure they work properly. It’s a good idea to test them after creating them and before sharing them with others. If the QR code is used often, test it every few weeks to ensure it scans correctly and links to the right content.
How Can I Test a QR Code Before Printing?
To test a QR code before printing, scan it with your smartphone or a QR code scanner app. Make sure it takes you to the correct link or shows the right information. Check the code from different angles and distances to ensure it easily scans and works as expected.
Conclusion
Testing a QR code is an important step to make sure it works correctly before sharing it. By using online tools, you can quickly check if the code links to the right website or performs the intended action. Fixing any errors early saves time and ensures a smooth experience for users. Following these simple steps will help you create a reliable and functional QR code every time.



![Software Test Plan Template with Detailed Explanation [Sample Test Plan Document]](https://www.softwaretestingmaterial.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/12/test-plan-template-768x432.png)